All Easy Linear Error in CoefM Object m Not Found
This browser is no longer supported.
Upgrade to Microsoft Edge to take advantage of the latest features, security updates, and technical support.
Resolve Resource Not Found errors
This article describes the error you see when a resource can't be found during an operation. Typically, you see this error when deploying resources with a Bicep file or Azure Resource Manager template (ARM template). You also see this error when doing management tasks and Azure Resource Manager can't find the required resource. For example, if you try to add tags to a resource that doesn't exist, you receive this error.
Symptoms
There are two error codes that indicate the resource can't be found. The NotFound error returns a result similar to:
Code=NotFound; Message=Cannot find ServerFarm with name exampleplan. The ResourceNotFound error returns a result similar to:
Code=ResourceNotFound; Message=The Resource 'Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/{storage name}' under resource group {resource group name} was not found. Cause
Resource Manager needs to retrieve the properties for a resource, but can't find the resource in your subscription.
Solution 1 - Check resource properties
When you receive this error while doing a management task, check the values you provided for the resource. The three values to check are:
- Resource name
- Resource group name
- Subscription
If you're using PowerShell or Azure CLI, check that you're running commands in the subscription that contains the resource. You can change the subscription with Set-AzContext or az account set. Many commands provide a subscription parameter that lets you specify a different subscription than the current context.
If you can't verify the properties, sign in to the Microsoft Azure portal. Find the resource you're trying to use and examine the resource name, resource group, and subscription.
Solution 2 - Set Dependencies
If you get this error when deploying a template, you may need to add a dependency. Resource Manager optimizes deployments by creating resources in parallel, when possible.
For example, when you deploy a web app, the App Service plan must exist. If you haven't specified that the web app depends on the App Service plan, Resource Manager creates both resources at the same time. The web app fails with an error that the App Service plan resource can't be found because it doesn't exist yet. You prevent this error by setting a dependency in the web app.
- Bicep
- JSON
Use an implicit dependency rather than the resourceId function. The dependency is created using a resource's symbolic name and ID property.
For example, the web app's serverFarmId property uses servicePlan.id to create a dependency on the App Service plan.
resource webApp 'Microsoft.Web/sites@2021-02-01' = { properties: { serverFarmId: servicePlan.id } } resource servicePlan 'Microsoft.Web/serverfarms@2021-02-01' = { name: hostingPlanName ... For most deployments, it's not necessary to use dependsOn to create an explicit dependency.
Avoid setting dependencies that aren't needed. Unnecessary dependencies prolong the deployment's duration because resources aren't deployed in parallel. Also, you might create circular dependencies that block the deployment.
Deployment order
When you see dependency problems, you need to gain insight into the order of resource deployment. You can use the portal to view the order of deployment operations:
-
Sign in to the portal.
-
From the resource group's Overview, select the link for the deployment history.

-
For the Deployment name you want to review, select Related events.
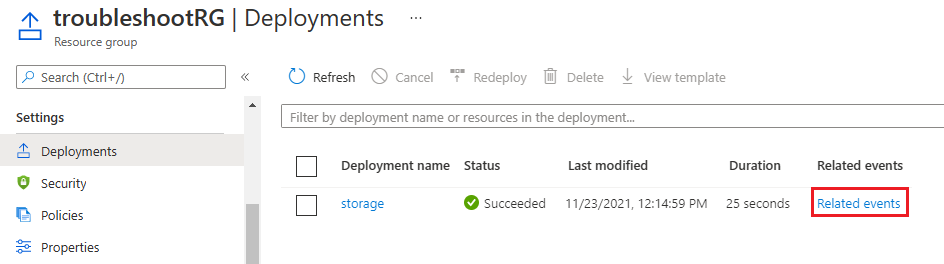
-
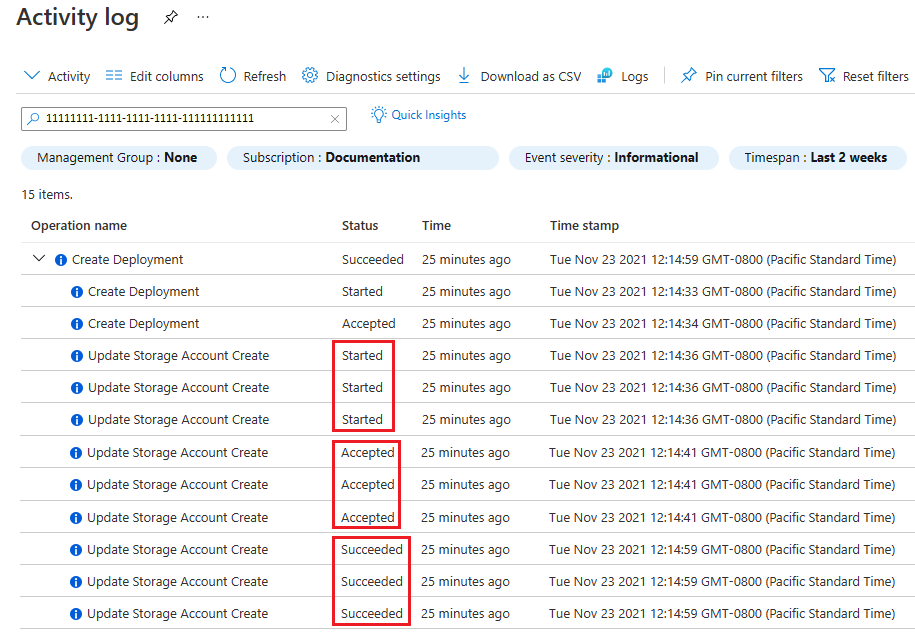
Examine the sequence of events for each resource. Pay attention to the status of each operation and it's time stamp. For example, the following image shows three storage accounts that deployed in parallel. Notice that the three storage accounts are started at the same time.
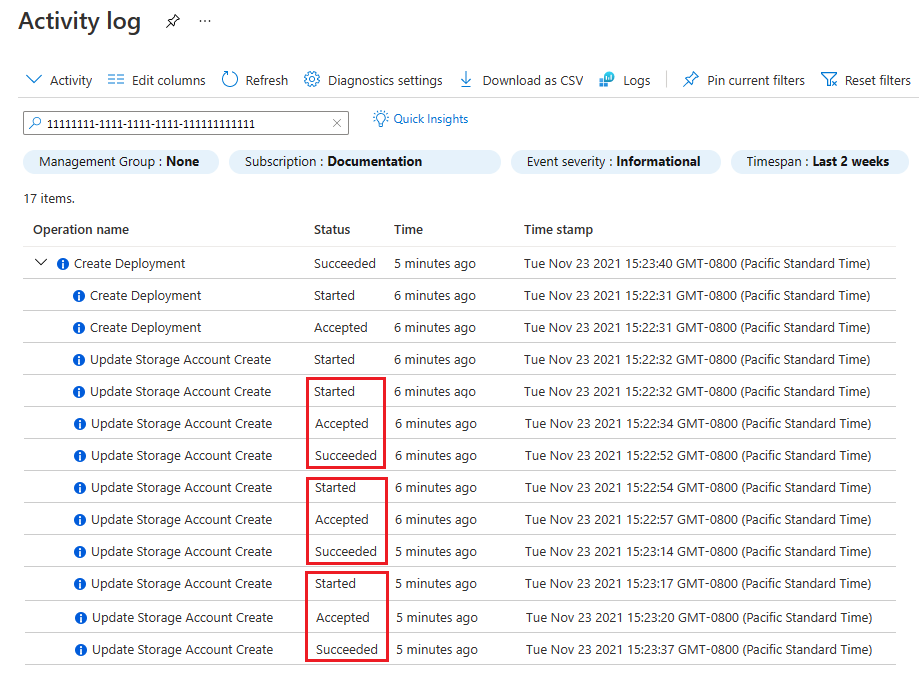
The next image shows three storage accounts that aren't deployed in parallel. The second storage account depends on the first storage account, and the third storage account depends on the second storage account. The first storage account is labeled Started, Accepted, and Succeeded before the next is started.
Solution 3 - Get external resource
- Bicep
- JSON
Bicep uses the symbolic name to create an implicit dependency on another resource. The existing keyword references a deployed resource. If an existing resource is in a different resource group than the resource you want to deploy, include scope and use the resourceGroup function.
In this example, a web app is deployed that uses an existing App Service plan from another resource group.
resource servicePlan 'Microsoft.Web/serverfarms@2021-02-01' existing = { name: hostingPlanName scope: resourceGroup(rgname) } resource webApp 'Microsoft.Web/sites@2021-02-01' = { name: siteName properties: { serverFarmId: servicePlan.id } } Solution 4 - Get managed identity from resource
- Bicep
- JSON
If you're deploying a resource with a managed identity, you must wait until that resource is deployed before retrieving values on the managed identity. Use an implicit dependency for the resource that the identity is applied to. This approach ensures the resource and the managed identity are deployed before Resource Manager uses the dependency.
You can get the principal ID and tenant ID for a managed identity that's applied to a virtual machine. For example, if a virtual machine resource has a symbolic name of vm, use the following syntax:
vm.identity.principalId vm.identity.tenantId Solution 5 - Check functions
- Bicep
- JSON
You can use a resource's symbolic name to get values from a resource. You can reference a storage account in the same resource group or another resource group using a symbolic name. To get a value from a deployed resource, use the existing keyword. If a resource is in a different resource group, use scope with the resourceGroup function. For most cases, the reference function isn't needed.
The following example references an existing storage account in a different resource group.
resource stgAcct 'Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts@2021-06-01' existing = { name: stgname scope: resourceGroup(rgname) } Solution 6 - After deleting resource
When you delete a resource, there might be a short amount of time when the resource appears in the portal but isn't available. If you select the resource, you'll get an error that the resource is Not found.
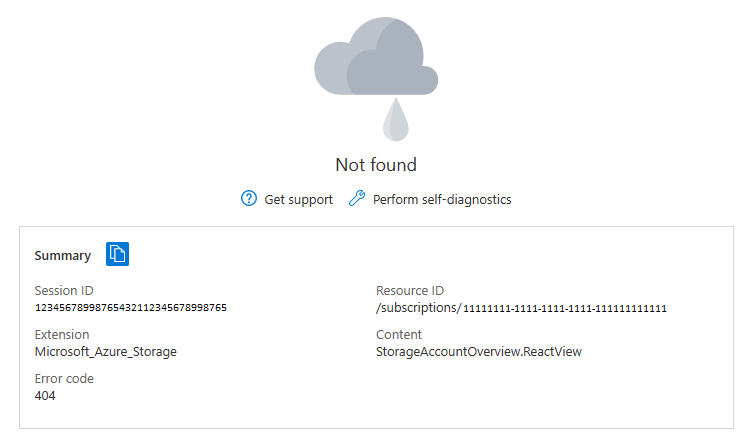
Refresh the portal and the deleted resource should be removed from your list of available resources. If a deleted resource continues to be shown as available for more than a few minutes, contact support.
Feedback
Submit and view feedback for
scarbroughupout1948.blogspot.com
Source: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-resource-manager/troubleshooting/error-not-found
0 Response to "All Easy Linear Error in CoefM Object m Not Found"
Post a Comment